copyright_author: 科学边界
copyright_author_href: https://www.daodaodao123.com/
copyright_info: 此文章版权归科学边界所有,如有转载,请注明来自原作者
copyright_url: https://www.daodaodao123.com/?p=740
Linux 初始化过程,会依次建立如下页表映射:
1. 恒等映射:页表基地址 idmap_pg_dir;
2. 粗粒度内核镜像映射:即上篇博文里的“第二次建立页表映射”,页表基地址 init_pg_dir;
3.fixmap 映射:页表基地址为 init_pg_dir, 待 paging_init 之后为 swapper_pg_end;
4. 细粒度内核镜像映射:页表基地址为 swapper_pg_dir;
5. 线性映射:页表基地址为 swapper_pg_dir;
6. 用户空间页表映射:页表基地址 task->mm->pgd;
上篇已经解析了 1 和 2 映射,这篇解析fixmap 映射。
void __init __no_sanitize_address setup_arch(char **cmdline_p)
{
///初始化,init_mm的地址,定义在arch/arm64/kernel/vmlinux.lds
setup_initial_init_mm(_stext, _etext, _edata, _end);
*cmdline_p = boot_command_line;
/*
* If know now we are going to need KPTI then use non-global
* mappings from the start, avoiding the cost of rewriting
* everything later.
*/
arm64_use_ng_mappings = kaslr_requires_kpti();
///注意这里都是创建的静态页表,因为内存子系统尚未建立(伙伴系统还没开始工作)
early_fixmap_init(); ///fixmap区映射,只创建中间级转换页表,最后一级页表未创建
early_ioremap_init(); ///早期ioremap映射,依赖fixmap转换表
/*
__fdt_pointer: fdt phy, ead.S中的__primary_switched阶段会执行str_l x21, __fdt_pointer, x5,将x21中的fdt地址存放到全局变量__fdt_pointer
setup_machine_fdt: 校验fdt合法性,并通过下面3个回调函数扫描fdt中预留的memory及传入内核参数
1. 扫描device tree函数:of_scan_flat_dt
2. 3个回调函数:
early_init_dt_scan_chosen: 解析chosen信息,其中一般包括initrd、bootargs,保留命令行参数到boot_command_line全局变量中
early_init_dt_scan_root: 从fdt中初始化{size, address}结构信息,保存到dt_root_addr_cells,dt_root_size_cells中
early_init_dt_scan_memory:扫描fdt中memory区域,寻找device_type="memory"的节点,并通过以下函数将该区域添加到memblock管理系统
early_init_dt_add_memory_arch
memblock_add:将region添加到memblock.memory中
*/
setup_machine_fdt(__fdt_pointer);
/*
* Initialise the static keys early as they may be enabled by the
* cpufeature code and early parameters.
*/
jump_label_init();
/*
解析boot_command_line, 并设置done标志位
*/
parse_early_param();
/*
* Unmask asynchronous aborts and fiq after bringing up possible
* earlycon. (Report possible System Errors once we can report this
* occurred).
*/
local_daif_restore(DAIF_PROCCTX_NOIRQ);
/*
* TTBR0 is only used for the identity mapping at this stage. Make it
* point to zero page to avoid speculatively fetching new entries.
*/
cpu_uninstall_idmap();
xen_early_init();
/*
* 1. 使用回调函数fdt_find_uefi_params获取fdt中关于uefi的信息,所有要扫描的参数包含在dt_param这个全局数组中
* 例如:system table, memmap address, memmap size, memmap desc. size, memmap desc. version
* 2. 将解析出的内存区域加入memblock.reserve区域
* 3. 调用uefi_init(), reserve_regions()等函数进行uefi模式初始化
* 4. 初始化完成后,将前面reserve的区域unreserve
*
*/
efi_init();
if (!efi_enabled(EFI_BOOT) && ((u64)_text % MIN_KIMG_ALIGN) != 0)
pr_warn(FW_BUG "Kernel image misaligned at boot, please fix your bootloader!");
///整理memblock的内存区域
arm64_memblock_init();
///至此,物理内存通过memblock模块添加入了系统,但此时只有dtb,Image所在的两段物理内存可以访问;
//其他区域的物理内存,还没建立映射,可以通过memblock_alloc分配,但不能访问;
//接下来通过paging_init建立不能访问的物理区域的页表;
//
//paging_init是内存初始化最核心的一步,将完成细粒度内核镜像映射(分别映射每个段),线性映射(内核可以访问整个物理内存)
paging_init(); ///建立动态页表
acpi_table_upgrade();
/* Parse the ACPI tables for possible boot-time configuration */
acpi_boot_table_init();
if (acpi_disabled)
/*
* 将dtb转换为device_node tree,根节点为全局变量 of_allnodes
* 后续内核会遍历tree来初始化描述的各个device
*/
unflatten_device_tree();
///至此,内核已经可以访问所有物理内存
///接下来开始初始化内存的关键数据结构,Linux当前默认采用sparse内存模型
bootmem_init();
kasan_init();
/*
* 将memblock.memory挂载到iomem_resource资源树下, 资源树是一颗倒挂的树
* request_resource:将设备实体登记注册到总线空间链
* 在遍历memblock.memory过程中,会检查kernel_code,kernel_data是否属于某region,如果是则挂载到该region下
*
*/
request_standard_resources();
/*
* early_ioremap 功能到此就结束了
* 在buddy系统还未建立前,要进行寄存器访问基本职能使用early_ioremap 功能
*/
early_ioremap_reset();
if (acpi_disabled)
psci_dt_init();
else
psci_acpi_init();
init_bootcpu_ops();
smp_init_cpus();
smp_build_mpidr_hash();
/* Init percpu seeds for random tags after cpus are set up. */
kasan_init_sw_tags();
#ifdef CONFIG_ARM64_SW_TTBR0_PAN
/*
* Make sure init_thread_info.ttbr0 always generates translation
* faults in case uaccess_enable() is inadvertently called by the init
* thread.
*/
init_task.thread_info.ttbr0 = phys_to_ttbr(__pa_symbol(reserved_pg_dir));
#endif
if (boot_args[1] || boot_args[2] || boot_args[3]) {
pr_err("WARNING: x1-x3 nonzero in violation of boot protocol:\n"
"\tx1: %016llx\n\tx2: %016llx\n\tx3: %016llx\n"
"This indicates a broken bootloader or old kernel\n",
boot_args[1], boot_args[2], boot_args[3]);
}
}
一、fixmap 映射的由来:
建立了恒等映射和粗粒度内核页表映射,只能保证内核镜像的正常访问,此时尚未建立内存管理子系统,如果想访问 bootloader 传入的 dtb,或者其他 io 设备,还是无法实现的,因此 Linux 提出了 fixmap.
fixmap:将一段 固定虚拟地址 映射到 dtb,以及想要访问的 IO 设备地址(比如串口,用于早期的打印调试);

二、fixmap 映射
源码参考 arch/arm64/kernel/setup.c 文件:
start_kernel()
->setup_arch()
->early_fixmap_init()
->early_ioramap_init()
->setup_machine_fdt(__fdt_pointer)
fix-mapped区域的基虚拟地址和大小由以下两个宏表示:
#define FIXADDR_SIZE (__end_of_permanent_fixed_addresses << PAGE_SHIFT)
#define FIXADDR_START (FIXADDR_TOP - FIXADDR_SIZE)
这里 __end_of_permanent_fixed_addresses 是fixed_addresses枚举的一个元素,每个固定映射地址都由在fixed_addresses中定义的整数索引表示。 PAGE_SHIFT确定页面的大小。例如,我们可以使用1 << PAGE_SHIFT表达式获得一页的大小。
我们需要获取固定映射区域的大小,但不仅仅是一页的大小,这就是我们使用的原因 __end_of_permanent_fixed_addresses 用于获取固定映射区域的大小。这 __end_of_permanent_fixed_addresses 是fixed_addresses枚举的最后一个索引,或者换句话说 __end_of_permanent_fixed_addresses 包含固定映射区域中的页面数量。所以如果我们乘以 __end_of_permanent_fixed_addresses 根据页面大小值,我们将获得固定映射区域的大小。它可能是一个不同的数字,因为大小取决于修复映射地址的数量,而修复映射地址的数量又取决于您的内核配置。
第二个FIXADDR_START宏只是从固定映射区域的最后一个地址中减去固定映射区域的大小,以获得其基虚拟地址。
#define FIXADDR_TOP (VMEMMAP_START - SZ_32M)
#define VMEMMAP_START (-(UL(1) << (VA_BITS - VMEMMAP_SHIFT)))
#define VMEMMAP_SHIFT (PAGE_SHIFT - STRUCT_PAGE_MAX_SHIFT)
#define STRUCT_PAGE_MAX_SHIFT (order_base_2(sizeof(struct page)))
2.1 early_fixmap_init 函数
void __init early_fixmap_init(void)
{
pgd_t *pgdp;
p4d_t *p4dp, p4d;
pud_t *pudp;
pmd_t *pmdp;
unsigned long addr = FIXADDR_START;
pgdp = pgd_offset_k(addr); /// 获得 pgd 页表项
p4dp = p4d_offset(pgdp, addr);
p4d = READ_ONCE(*p4dp);
if (CONFIG_PGTABLE_LEVELS> 3 &&
!(p4d_none(p4d) || p4d_page_paddr(p4d) == __pa_symbol(bm_pud))) {
/*
* We only end up here if the kernel mapping and the fixmap
* share the top level pgd entry, which should only happen on
* 16k/4 levels configurations.
*/
BUG_ON(!IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_ARM64_16K_PAGES));
pudp = pud_offset_kimg(p4dp, addr);
} else {if (p4d_none(p4d))
__p4d_populate(p4dp, __pa_symbol(bm_pud), P4D_TYPE_TABLE); /// 填充 p4d 表项
pudp = fixmap_pud(addr); /// 获得 pud 表项
}
if (pud_none(READ_ONCE(*pudp)))
__pud_populate(pudp, __pa_symbol(bm_pmd), PUD_TYPE_TABLE); /// 填充 pud 表项
pmdp = fixmap_pmd(addr);
__pmd_populate(pmdp, __pa_symbol(bm_pte), PMD_TYPE_TABLE); /// 填充 pmd 表项
/*
* The boot-ioremap range spans multiple pmds, for which
* we are not prepared:
*/
BUILD_BUG_ON((__fix_to_virt(FIX_BTMAP_BEGIN) >> PMD_SHIFT)
!= (__fix_to_virt(FIX_BTMAP_END) >> PMD_SHIFT));
if ((pmdp != fixmap_pmd(fix_to_virt(FIX_BTMAP_BEGIN)))
|| pmdp != fixmap_pmd(fix_to_virt(FIX_BTMAP_END))) {WARN_ON(1);
pr_warn("pmdp %p != %p, %p\n",
pmdp, fixmap_pmd(fix_to_virt(FIX_BTMAP_BEGIN)),
fixmap_pmd(fix_to_virt(FIX_BTMAP_END)));
pr_warn("fix_to_virt(FIX_BTMAP_BEGIN): %08lx\n",
fix_to_virt(FIX_BTMAP_BEGIN));
pr_warn("fix_to_virt(FIX_BTMAP_END): %08lx\n",
fix_to_virt(FIX_BTMAP_END));
pr_warn("FIX_BTMAP_END: %d\n", FIX_BTMAP_END);
pr_warn("FIX_BTMAP_BEGIN: %d\n", FIX_BTMAP_BEGIN);
}
}
fix_to_virt函数使用fixed_addresses枚举作为索引来获取虚拟地址。这个函数的实现很简单
static __always_inline unsigned long fix_to_virt(const unsigned int idx)
{
BUILD_BUG_ON(idx >= __end_of_fixed_addresses);
return __fix_to_virt(idx);
}
#define __fix_to_virt(x) (FIXADDR_TOP - ((x) << PAGE_SHIFT))
首先,它使用BUILD_BUG_ON宏检查为fixed_addresses枚举指定的索引是否不大于或等于__end_of_fixed_addresses ,然后返回__fix_to_virt宏的结果
我们将PAGE_SHIFT上的fix-mapped区域的给定索引左移,该索引确定页面的大小,如我上面所写,并从FIXADDR_TOP fix-mapped区域的最高地址)中减去它:
+-----------------+
| PAGE 1 | FIXADDR_TOP (virt address)
| PAGE 2 |
| PAGE 3 |
| PAGE 4 (idx) | x - 4
| PAGE 5 |
+-----------------+
有一个反函数用于获取与给定虚拟地址相对应的固定映射区域的索引:
static inline unsigned long virt_to_fix(const unsigned long vaddr)
{
BUG_ON(vaddr >= FIXADDR_TOP || vaddr < FIXADDR_START);
return __virt_to_fix(vaddr);
}
#define __virt_to_fix(x) ((FIXADDR_TOP - ((x)&PAGE_MASK)) >> PAGE_SHIFT)
virt_to_fix获取一个虚拟地址,检查该地址是否在FIXADDR_START和FIXADDR_TOP之间,并调用__virt_to_fix宏。
与前面的示例(在__fix_to_virt宏中)一样,我们从修复映射区域的顶部开始。我们还从上到下搜索与给定虚拟地址对应的固定映射区域的索引。正如您所看到的,首先我们将使用x & PAGE_MASK表达式清除给定虚拟地址中的前12位。这使我们能够获取页面的基地址。当给定的虚拟地址指向页面的开头/中间或结尾的某个位置但不是其基地址时,我们需要执行此操作。在下一步中,从FIXADDR_TOP中减去该值,这将为我们提供固定映射区域中相应页面的虚拟地址。最后我们只需将该地址的值除以PAGE_SHIFT即可。这为我们提供了与给定虚拟地址相对应的固定映射区域的索引。
三、ioremap
3.1early_ioremap_init 函数
void __init early_ioremap_setup(void)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < FIX_BTMAPS_SLOTS; i++)
if (WARN_ON(prev_map[i]))
break;
for (i = 0; i < FIX_BTMAPS_SLOTS; i++)
slot_virt[i] = __fix_to_virt(FIX_BTMAP_BEGIN - NR_FIX_BTMAPS*i); /// 根据索引,得到虚拟地址
}
上述填充完页表和计算准备虚拟地址,在 early_ioremap 函数,实际建立映射关系;
3.2 early_ioremap 函数
static void __init __iomem *
__early_ioremap(resource_size_t phys_addr, unsigned long size, pgprot_t prot)
{
unsigned long offset;
resource_size_t last_addr;
unsigned int nrpages;
enum fixed_addresses idx;
int i, slot;
WARN_ON(system_state>= SYSTEM_RUNNING);
slot = -1;
for (i = 0; i < FIX_BTMAPS_SLOTS; i++) {if (!prev_map[i]) {
slot = i;
break;
}
}
if (WARN(slot < 0, "%s(%pa, %08lx) not found slot\n",
__func__, &phys_addr, size))
return NULL;
/* Don't allow wraparound or zero size */
last_addr = phys_addr + size - 1;
if (WARN_ON(!size || last_addr < phys_addr))
return NULL;
prev_size[slot] = size;
/*
* Mappings have to be page-aligned
*/
offset = offset_in_page(phys_addr);
phys_addr &= PAGE_MASK;
size = PAGE_ALIGN(last_addr + 1) - phys_addr;
/*
* Mappings have to fit in the FIX_BTMAP area.
*/
nrpages = size >> PAGE_SHIFT;
if (WARN_ON(nrpages> NR_FIX_BTMAPS))
return NULL;
/*
* Ok, go for it..
*/
idx = FIX_BTMAP_BEGIN - NR_FIX_BTMAPS*slot;
while (nrpages> 0) {if (after_paging_init)
__late_set_fixmap(idx, phys_addr, prot);
else
__early_set_fixmap(idx, phys_addr, prot); /// 建立虚拟地址到 phys_addr 的映射
phys_addr += PAGE_SIZE;
--idx;
--nrpages;
}
WARN(early_ioremap_debug, "%s(%pa, %08lx) [%d] => %08lx + %08lx\n",
__func__, &phys_addr, size, slot, offset, slot_virt[slot]);
prev_map[slot] = (void __iomem *)(offset + slot_virt[slot]); /// 返回实际的虚拟地址
return prev_map[slot];
}
3.3 earlycon
在 driver/tty/serail/earlycon.c 文件,earlycon_map 函数实际做 ioremap 映射
static void __iomem * __init earlycon_map(resource_size_t paddr, size_t size)
{
void __iomem *base;
#ifdef CONFIG_FIX_EARLYCON_MEM
set_fixmap_io(FIX_EARLYCON_MEM_BASE, paddr & PAGE_MASK);
base = (void __iomem *)__fix_to_virt(FIX_EARLYCON_MEM_BASE);
base += paddr & ~PAGE_MASK;
#else
base = ioremap(paddr, size);
#endif
if (!base)
pr_err("%s: Couldn't map %pa\n", __func__, &paddr);
return base;
}
四、dtb 映射
设备树,通过虚拟地址获取内存信息和板级信息;
setup_machine_fdt(__fdt_pointer);/// 设备树映射
static void __init setup_machine_fdt(phys_addr_t dt_phys)
{
int size;
///完成fdt的pte页表填写,返回fdt虚拟地址,这里虚拟地址事先定义预留
///映射了2MB
void *dt_virt = fixmap_remap_fdt(dt_phys, &size, PAGE_KERNEL);
const char *name;
if (dt_virt)
///把dtb所占内存添加到memblock管理的reserve模块,后续内存分配不会使用这段内存
//使用完后,会使用memblock_free()释放
memblock_reserve(dt_phys, size);
///扫描解析dtb,将内存布局信息填入memblock系统
if (!dt_virt || !early_init_dt_scan(dt_virt)) {
pr_crit("\n"
"Error: invalid device tree blob at physical address %pa (virtual address 0x%p)\n"
"The dtb must be 8-byte aligned and must not exceed 2 MB in size\n"
"\nPlease check your bootloader.",
&dt_phys, dt_virt);
while (true)
cpu_relax();
}
/* Early fixups are done, map the FDT as read-only now */
fixmap_remap_fdt(dt_phys, &size, PAGE_KERNEL_RO);
name = of_flat_dt_get_machine_name();
if (!name)
return;
pr_info("Machine model: %s\n", name);
dump_stack_set_arch_desc("%s (DT)", name);
}
4.1 fixmap_remap_fdt
void *__init fixmap_remap_fdt(phys_addr_t dt_phys, int *size, pgprot_t prot)
{
///完成fdt的pte页表填写,返回fdt虚拟地址,这里虚拟地址事先定义预留
const u64 dt_virt_base = __fix_to_virt(FIX_FDT); ///获得设备树的虚拟地址
int offset;
void *dt_virt;
/*
* Check whether the physical FDT address is set and meets the minimum
* alignment requirement. Since we are relying on MIN_FDT_ALIGN to be
* at least 8 bytes so that we can always access the magic and size
* fields of the FDT header after mapping the first chunk, double check
* here if that is indeed the case.
*/
BUILD_BUG_ON(MIN_FDT_ALIGN < 8);
if (!dt_phys || dt_phys % MIN_FDT_ALIGN)
return NULL;
/*
* Make sure that the FDT region can be mapped without the need to
* allocate additional translation table pages, so that it is safe
* to call create_mapping_noalloc() this early.
*
* On 64k pages, the FDT will be mapped using PTEs, so we need to
* be in the same PMD as the rest of the fixmap.
* On 4k pages, we'll use section mappings for the FDT so we only
* have to be in the same PUD.
*/
BUILD_BUG_ON(dt_virt_base % SZ_2M);
///early_fixmap_init已经建立了pud,pmd,保证fdt所在虚拟地址范围,在范围内,
BUILD_BUG_ON(__fix_to_virt(FIX_FDT_END) >> SWAPPER_TABLE_SHIFT !=
__fix_to_virt(FIX_BTMAP_BEGIN) >> SWAPPER_TABLE_SHIFT);
offset = dt_phys % SWAPPER_BLOCK_SIZE;
dt_virt = (void *)dt_virt_base + offset;
/* map the first chunk so we can read the size from the header */
//根据提供的物理地址和虚拟地址,设置页表项
//建立映射,页表物理地址已知的,不能临时分配(因为伙伴系统尚未工作)
create_mapping_noalloc(round_down(dt_phys, SWAPPER_BLOCK_SIZE),
dt_virt_base, SWAPPER_BLOCK_SIZE, prot);
///根据虚拟地址访问物理地址内容(fdt内容),检测dtb文件头的魔数是否正确
if (fdt_magic(dt_virt) != FDT_MAGIC)
return NULL;
*size = fdt_totalsize(dt_virt);
if (*size > MAX_FDT_SIZE)
return NULL;
///如果dtb文件尾地址空间超过了2MB, 再紧接着再映射一个2m地址空间
if (offset + *size > SWAPPER_BLOCK_SIZE)
create_mapping_noalloc(round_down(dt_phys, SWAPPER_BLOCK_SIZE), dt_virt_base,
round_up(offset + *size, SWAPPER_BLOCK_SIZE), prot);
return dt_virt;
}
4.2 memblock_reserve
把dtb所占内存添加到memblock管理的reserve模块,后续内存分配不会使用这段内存,使用完后,会使用memblock_free()释放
int __init_memblock memblock_reserve(phys_addr_t base, phys_addr_t size)
{
phys_addr_t end = base + size - 1;
memblock_dbg("%s: [%pa-%pa] %pS\n", __func__,
&base, &end, (void *)_RET_IP_);
return memblock_add_range(&memblock.reserved, base, size, MAX_NUMNODES, 0);
}
4.3 early_init_dt_scan
early_init_dt_scan //扫描解析dtb,将内存布局信息填入memblock系统
-> early_init_dt_scan_nodes
void __init early_init_dt_scan_nodes(void)
{
int rc = 0;
/* Initialize {size,address}-cells info */
of_scan_flat_dt(early_init_dt_scan_root, NULL);
/* Retrieve various information from the /chosen node */
/*
* 扫描chosen节点,把bootargs值拷贝到boot_command_line中,
* 如果定义了CONFIG_CMDLINE宏,把命令行参数拷贝到boot_command_line
* */
rc = of_scan_flat_dt(early_init_dt_scan_chosen, boot_command_line);
if (!rc)
pr_warn("No chosen node found, continuing without\n");
/* Setup memory, calling early_init_dt_add_memory_arch */
///对dtb中的memory node进行解析
of_scan_flat_dt(early_init_dt_scan_memory, NULL);
/* Handle linux,usable-memory-range property */
memblock_cap_memory_range(cap_mem_addr, cap_mem_size);
}
4.3.1 early_init_dt_scan_chosen
int __init early_init_dt_scan_chosen(unsigned long node, const char *uname,
int depth, void *data)
{
int l;
const char *p;
const void *rng_seed;
pr_debug("search \"chosen\", depth: %d, uname: %s\n", depth, uname);
if (depth != 1 || !data ||
(strcmp(uname, "chosen") != 0 && strcmp(uname, "chosen@0") != 0))
return 0;
early_init_dt_check_for_initrd(node);
early_init_dt_check_for_elfcorehdr(node);
early_init_dt_check_for_usable_mem_range(node);
/* Retrieve command line */
// 获取bootargs
p = of_get_flat_dt_prop(node, "bootargs", &l);
if (p != NULL && l > 0)
strlcpy(data, p, min(l, COMMAND_LINE_SIZE));
/*
* CONFIG_CMDLINE is meant to be a default in case nothing else
* managed to set the command line, unless CONFIG_CMDLINE_FORCE
* is set in which case we override whatever was found earlier.
*/
#ifdef CONFIG_CMDLINE
#if defined(CONFIG_CMDLINE_EXTEND)
strlcat(data, " ", COMMAND_LINE_SIZE);
strlcat(data, CONFIG_CMDLINE, COMMAND_LINE_SIZE);
#elif defined(CONFIG_CMDLINE_FORCE)
strlcpy(data, CONFIG_CMDLINE, COMMAND_LINE_SIZE);
#else
/* No arguments from boot loader, use kernel's cmdl*/
if (!((char *)data)[0])
strlcpy(data, CONFIG_CMDLINE, COMMAND_LINE_SIZE);
#endif
#endif /* CONFIG_CMDLINE */
pr_debug("Command line is: %s\n", (char *)data);
rng_seed = of_get_flat_dt_prop(node, "rng-seed", &l);
if (rng_seed && l > 0) {
add_bootloader_randomness(rng_seed, l);
/* try to clear seed so it won't be found. */
fdt_nop_property(initial_boot_params, node, "rng-seed");
/* update CRC check value */
of_fdt_crc32 = crc32_be(~0, initial_boot_params,
fdt_totalsize(initial_boot_params));
}
/* break now */
return 1;
}
4.3.2 early_init_dt_scan_memory
int __init early_init_dt_scan_memory(unsigned long node, const char *uname,
int depth, void *data)
{
const char *type = of_get_flat_dt_prop(node, "device_type", NULL);
const __be32 *reg, *endp;
int l;
bool hotpluggable;
/* We are scanning "memory" nodes only */
if (type == NULL || strcmp(type, "memory") != 0)
return 0;
reg = of_get_flat_dt_prop(node, "linux,usable-memory", &l);
if (reg == NULL)
reg = of_get_flat_dt_prop(node, "reg", &l);
if (reg == NULL)
return 0;
endp = reg + (l / sizeof(__be32));
hotpluggable = of_get_flat_dt_prop(node, "hotpluggable", NULL);
pr_debug("memory scan node %s, reg size %d,\n", uname, l);
while ((endp - reg) >= (dt_root_addr_cells + dt_root_size_cells)) {
u64 base, size;
base = dt_mem_next_cell(dt_root_addr_cells, ®);
size = dt_mem_next_cell(dt_root_size_cells, ®);
if (size == 0)
continue;
pr_debug(" - %llx, %llx\n", base, size);
///向系统注册该memory node内存区域, 通过memblock_add完成添加
early_init_dt_add_memory_arch(base, size);
if (!hotpluggable)
continue;
if (memblock_mark_hotplug(base, size))
pr_warn("failed to mark hotplug range 0x%llx - 0x%llx\n",
base, base + size);
}
return 0;
}
五、memblock的初始化
紧接上文dtb映射之后,setup_arch函数走到了memblock的初始化流程
/*
* 整理内存区域,将一些特殊区域添加到memblock内存管理模块中
* 移除不归内核管理的区域(dts的no-map区域),还申请一个公共区域的CMA
*
* 最终通过memblock模块,把内存中的空闲和被占用的区域进行分开管理
*
* */
void __init arm64_memblock_init(void)
{
///计算虚拟地址可以覆盖的线性区域
s64 linear_region_size = PAGE_END - _PAGE_OFFSET(vabits_actual);
/*
* Corner case: 52-bit VA capable systems running KVM in nVHE mode may
* be limited in their ability to support a linear map that exceeds 51
* bits of VA space, depending on the placement of the ID map. Given
* that the placement of the ID map may be randomized, let's simply
* limit the kernel's linear map to 51 bits as well if we detect this
* configuration.
*/
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_KVM) && vabits_actual == 52 &&
is_hyp_mode_available() && !is_kernel_in_hyp_mode()) {
pr_info("Capping linear region to 51 bits for KVM in nVHE mode on LVA capable hardware.\n");
linear_region_size = min_t(u64, linear_region_size, BIT(51));
}
///移除实际物理地址以上的内存空间区域,比如VA_BITS=48,大于2^48以上地址,memblock不必存在
/* Remove memory above our supported physical address size */
memblock_remove(1ULL << PHYS_MASK_SHIFT, ULLONG_MAX);
/*
* Select a suitable value for the base of physical memory.
*/
///物理地址起始地址,尚未memblock_add,此处为0
memstart_addr = round_down(memblock_start_of_DRAM(),
ARM64_MEMSTART_ALIGN);
if ((memblock_end_of_DRAM() - memstart_addr) > linear_region_size)
pr_warn("Memory doesn't fit in the linear mapping, VA_BITS too small\n");
/*
* Remove the memory that we will not be able to cover with the
* linear mapping. Take care not to clip the kernel which may be
* high in memory.
*/
///移除线性映射以外的内存
memblock_remove(max_t(u64, memstart_addr + linear_region_size,
__pa_symbol(_end)), ULLONG_MAX);
///如果物理内存足够大,将虚拟地址无法覆盖的区域删除掉
if (memstart_addr + linear_region_size < memblock_end_of_DRAM()) {
/* ensure that memstart_addr remains sufficiently aligned */
memstart_addr = round_up(memblock_end_of_DRAM() - linear_region_size,
ARM64_MEMSTART_ALIGN);
memblock_remove(0, memstart_addr);
}
/*
* If we are running with a 52-bit kernel VA config on a system that
* does not support it, we have to place the available physical
* memory in the 48-bit addressable part of the linear region, i.e.,
* we have to move it upward. Since memstart_addr represents the
* physical address of PAGE_OFFSET, we have to *subtract* from it.
*/
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_ARM64_VA_BITS_52) && (vabits_actual != 52))
memstart_addr -= _PAGE_OFFSET(48) - _PAGE_OFFSET(52);
/*
* Apply the memory limit if it was set. Since the kernel may be loaded
* high up in memory, add back the kernel region that must be accessible
* via the linear mapping.
*/
///如果limit被配置,根据meory_limit重新配置,一般不会配置
if (memory_limit != PHYS_ADDR_MAX) {
memblock_mem_limit_remove_map(memory_limit);
memblock_add(__pa_symbol(_text), (u64)(_end - _text));
}
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_BLK_DEV_INITRD) && phys_initrd_size) {
/*
* Add back the memory we just removed if it results in the
* initrd to become inaccessible via the linear mapping.
* Otherwise, this is a no-op
*/
u64 base = phys_initrd_start & PAGE_MASK;
u64 size = PAGE_ALIGN(phys_initrd_start + phys_initrd_size) - base;
/*
* We can only add back the initrd memory if we don't end up
* with more memory than we can address via the linear mapping.
* It is up to the bootloader to position the kernel and the
* initrd reasonably close to each other (i.e., within 32 GB of
* each other) so that all granule/#levels combinations can
* always access both.
*/
if (WARN(base < memblock_start_of_DRAM() ||
base + size > memblock_start_of_DRAM() +
linear_region_size,
"initrd not fully accessible via the linear mapping -- please check your bootloader ...\n")) {
phys_initrd_size = 0;
} else {
///如果initrd地址符合要求,重新加入memblock.memory,且reserved这块内存
memblock_remove(base, size); /* clear MEMBLOCK_ flags */
memblock_add(base, size);
memblock_reserve(base, size);
}
}
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_RANDOMIZE_BASE)) {
extern u16 memstart_offset_seed;
u64 mmfr0 = read_cpuid(ID_AA64MMFR0_EL1);
int parange = cpuid_feature_extract_unsigned_field(
mmfr0, ID_AA64MMFR0_PARANGE_SHIFT);
s64 range = linear_region_size -
BIT(id_aa64mmfr0_parange_to_phys_shift(parange));
/*
* If the size of the linear region exceeds, by a sufficient
* margin, the size of the region that the physical memory can
* span, randomize the linear region as well.
*/
if (memstart_offset_seed > 0 && range >= (s64)ARM64_MEMSTART_ALIGN) {
range /= ARM64_MEMSTART_ALIGN;
memstart_addr -= ARM64_MEMSTART_ALIGN *
((range * memstart_offset_seed) >> 16);
}
}
/*
* Register the kernel text, kernel data, initrd, and initial
* pagetables with memblock.
*/
///将内核设置为reserved类型
///paging_init()后会释放
memblock_reserve(__pa_symbol(_stext), _end - _stext);
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_BLK_DEV_INITRD) && phys_initrd_size) {
///计算initrd对应虚拟地址
/* the generic initrd code expects virtual addresses */
initrd_start = __phys_to_virt(phys_initrd_start);
initrd_end = initrd_start + phys_initrd_size;
}
///扫描dtb中的reserved-memory节点,将每个子结点添加到memblock.reserved,设置为reserved类型
///如果节点定义了nomap,会从memblock.memory删除,就像物理上没有这片内存
///cma具有reuseable属性,则不会从memblock.memory删除
early_init_fdt_scan_reserved_mem();
///ARM64中不需要高端内存,为了向前兼容,这里将高端内存的起始地址设置为物理内存的结束地址
high_memory = __va(memblock_end_of_DRAM() - 1) + 1;
}
5.1 early_init_fdt_scan_reserved_mem
扫描dtb中的reserved-memory节点,将每个子结点添加到memblock.reserved,设置为reserved类型
void __init early_init_fdt_scan_reserved_mem(void)
{
int n;
u64 base, size;
if (!initial_boot_params)
return;
/* Process header /memreserve/ fields */
for (n = 0; ; n++) {
/* 通过fdt_header.off_mem_rsvmap指针,找出/memreserve/ fields的base & size */
fdt_get_mem_rsv(initial_boot_params, n, &base, &size);
if (!size)
break;
//将dtb区域加入memblock.reserve, initial_boot_params=fdt
early_init_dt_reserve_memory_arch(base, size, false);
}
/*将/reserved-memory/ fields 加入memblock.reserve, 并将其保存到全局数组reserved_mem*/
of_scan_flat_dt(__fdt_scan_reserved_mem, NULL);
/* 将/reserved-memory/ fields 分配内存空间 */
fdt_init_reserved_mem();
fdt_reserve_elfcorehdr();
}
5.2 __fdt_scan_reserved_mem
__fdt_scan_reserved_mem是用来查找设备树中的reserved-memory属性的节点的
static int __init __fdt_scan_reserved_mem(unsigned long node, const char *uname,
int depth, void *data)
{
static int found;
int err;
if (!found && depth == 1 && strcmp(uname, "reserved-memory") == 0) {
if (__reserved_mem_check_root(node) != 0) {
pr_err("Reserved memory: unsupported node format, ignoring\n");
/* break scan */
return 1;
}
found = 1;
/* scan next node */
return 0;
} else if (!found) {
/* scan next node */
return 0;
} else if (found && depth < 2) {
/* scanning of /reserved-memory has been finished */
return 1;
}
if (!of_fdt_device_is_available(initial_boot_params, node))
return 0;
err = __reserved_mem_reserve_reg(node, uname);
if (err == -ENOENT && of_get_flat_dt_prop(node, "size", NULL))
fdt_reserved_mem_save_node(node, uname, 0, 0);
/* scan next node */
return 0;
}
搜索设备树可以获知这些reserved-memory
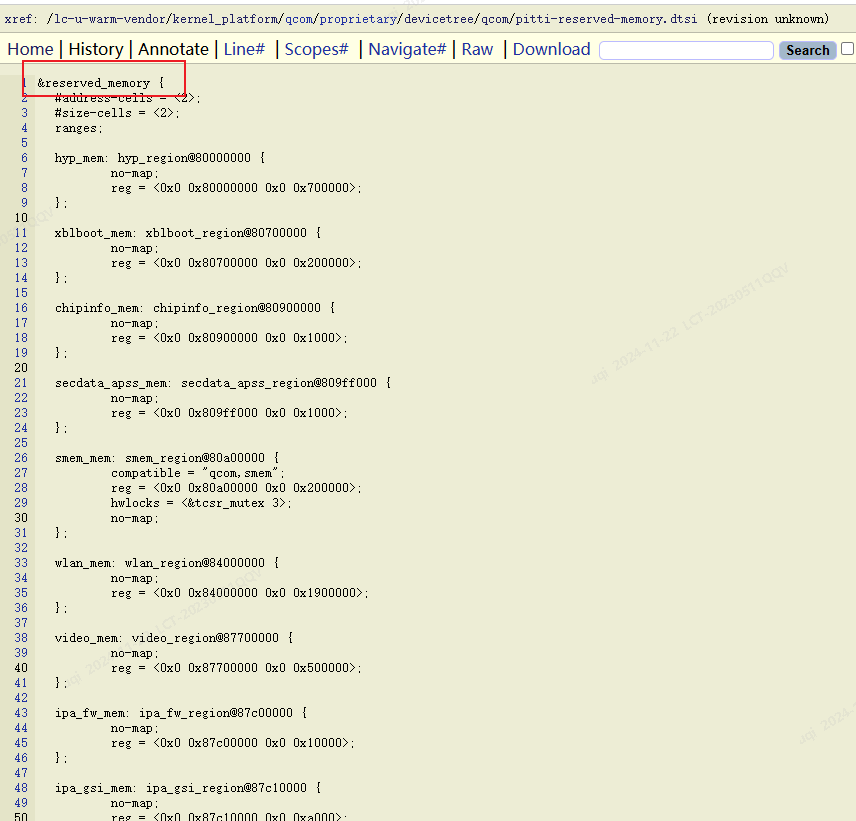
六、总结
在看paging_init()函数前,我们先看下目前的内存状态
{% tip success %}
目前所有的内存分为了2部分
OS已经收集到的内存分布信息(来自dtb解析),保存在memblock中,这部分又分为3个小部分
系统内存占据的空间,信息保存在memblock.memory中
已经使用或者保留使用的,信息保存在memblock.reserve中
dtb中reserved-memory,但是有No-map属性,这种内存不属于OS管辖
OS还未收集到的内存部分,暂未管辖(这部分稍后会被加载到伙伴系统中)
在目前状态下,OS还无法正常使用它们,因为memblock中定义的都是物理地址;而目前仅有两段内存是已经mapping过(kernel image, fdt),其余段都还是黑暗状态,接下来就要给第一部分内存做mapping
{% endtip %}
物理内存通过memblock模块添加入了系统,但此时只有dtb,Image所在的两段物理内存可以访问;其他区域的物理内存,还没建立映射,可以通过memblock_alloc分配,但不能访问;接下来通过paging_init建立不能访问的物理区域的页表; paging_init是内存初始化最核心的一步,将完成细粒度内核镜像映射(分别映射每个段),线性映射(内核可以访问整个物理内存)。
由于本篇篇幅过长,所以这一阶段放在下一章节继续。
